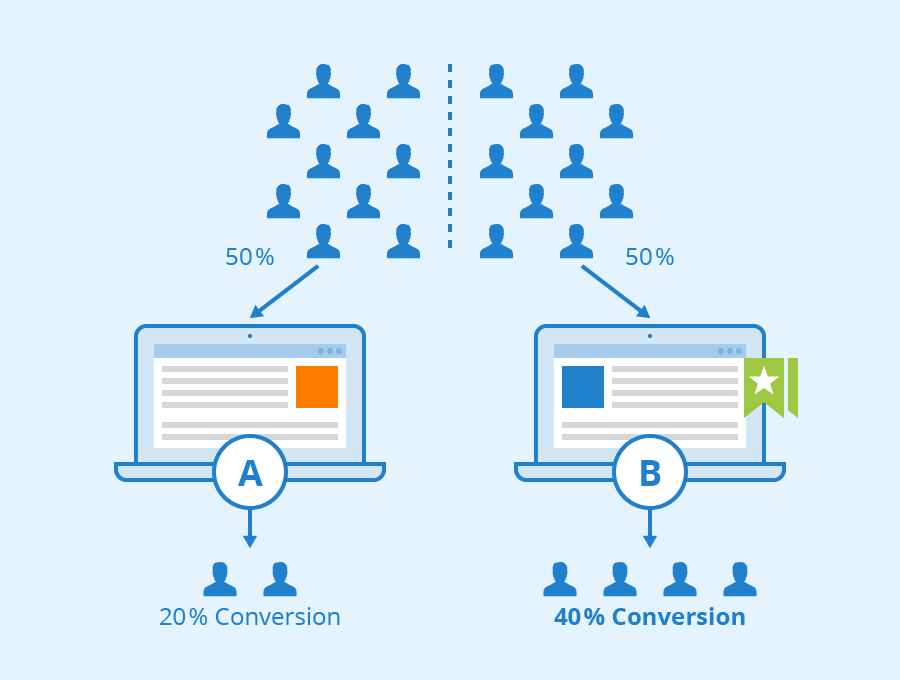
A/B testing, commonly referred to as split testing, is a marketing experiment in which you divide your audience in half to test various campaign iterations and see which one performs best. In other words, you can show one half of your audience version A of a piece of marketing content while showing the other half version B.
Every product manager should be familiar with A/B testing, which enables businesses to assess their consumers with more thorough data. Users may identify the things they need by becoming more familiar with A/B Testing, which considers the customer experience by examining which keys, how frequently, and other factors.
A/B testing should be used by product managers. Because they need to employ A/B testing to properly accomplish tasks like figuring out consumer demands and the business and flow aim of a product or feature, outlining what a product's success criteria are, and turning a product's vision into reality.
There are many benefits to using A/B tests, including:
- Product managers can focus on very specific elements to test
- Test results' precision is usually very high
- A/B tests examine actual engagement with the asset, in contrast to surveys where users' responses are hypothetical.
Better User Engagement
A/B testing is a clever strategy to enhance your website's content and boost interaction. A/B testing assists you in making changes to your content that increase engagement when you evaluate the findings of a test and use them to guide your future selections. You may test the color of a button on your website or mobile application, for instance. The color that generates the most clicks can then be observed. It's amazing how much of an impact a simple modification can have on engagement. Once the A/B test has been completed, you may determine which variation performs better and preserve it.
Many situations allow for the usage of A/B testing. This tool can be used by product developers and designers to improve user experiences by changing particular page elements to produce a new design variation. A/B testing is necessary for user engagement, onboarding, modals, and in-product experiences, but it is only successful when objectives are established beforehand and hypotheses are tested.
How to do A/B testing ?
A/B testing is separated into three phases: before, during, and after.
Stage 1: Before A/B Testing
- Determine which parameters you need to measure with A/B testing
- Determine your target market into two equal and diverse groups
- To achieve excellent test accuracy, start the tests at the same time (The test may deviate as a result of the time difference.)
Stage 2: During A/B Testing
- Use an A/B Testing tool
- Give enough time for both tests
- Get feedback from your potential users
Stage 3: After A/B Testing
- Make sure the findings is correct
- Based on your findings, make action plans
- Put the next feature/plugin to the test that will be put to the test
All features and plugins of an application should not be tested. The company can lose time by doing this. First, any criteria that are identified as being significant to the business should then be examined. However, not all parameters ought to be examined simultaneously. Then, a proper roadmap should be used to place the tests, and that roadmap should be followed step by step when implementing the application.
In Summary
By bringing the product in two separate modules together with potential consumers and collecting the feedback from them, it is a test that aids in the creation of product features and add-ons. A/B testing is a gradual process, and when it is carried out properly, the test findings are more accurate. Every test that uses A/B testing brings the product one step closer to being a success.
Producter is a product management tool designed to become customer-driven.
It helps you collect feedback, manage tasks, sharing product updates, creating product docs, and tracking roadmap.






