A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is just what it sounds like. Introducing a new product to the market with minimal features but enough to catch consumer attention is called Minimum Viable Product or MVP. After the first product users provide enough feedback, the final product is released to the market.
A minimum viable product (MVP) is designed to attract early adopters and validate a product idea early on. When a product has enough features to attract customers early in its development cycle, it’s time for the MVP to be released. It is particularly useful in the software development vertical, where product teams need to iterate and improve the product by collecting user feedback.
The MVP approach is widely adopted by product teams. This approach does have some drawbacks, as outlined above. Providing the bare minimum may not be enough to draw and engage customers in the long run. Likewise, it may not meet the needs of markets with many options and customers with higher expectations. So, building a Minimum Lovable Product (MLP) will most likely achieve better results than developing an MVP.
The Lean Approach to MVP/MLP
The lean methodology involves building as few products as possible and seeking answers. To validate your product idea, you must test your hypothesis in the market. You can validate it by having a one-on-one conversation, creating surveys, and building lean beta versions. Product managers should benefit from the lean approach by avoiding the build trap. It also prevents the product and team from being affected by the failure. In other words, you save both time and resources.
In the early stages of development, launching a Minimal Viable Product (MVP) helps teams get user feedback and find the Product-Market Fit as quickly as possible. An alternative concept is Minimal Loveable Product (MLP), which aims to determine how much buzz and excitement a product will generate in the market. In both cases, you do not want to invest all your resources in building out a complete product before determining whether or not it will succeed. In Lean methodology, MVP and MLP are ways to get feedback early and often instead of waiting until the end.
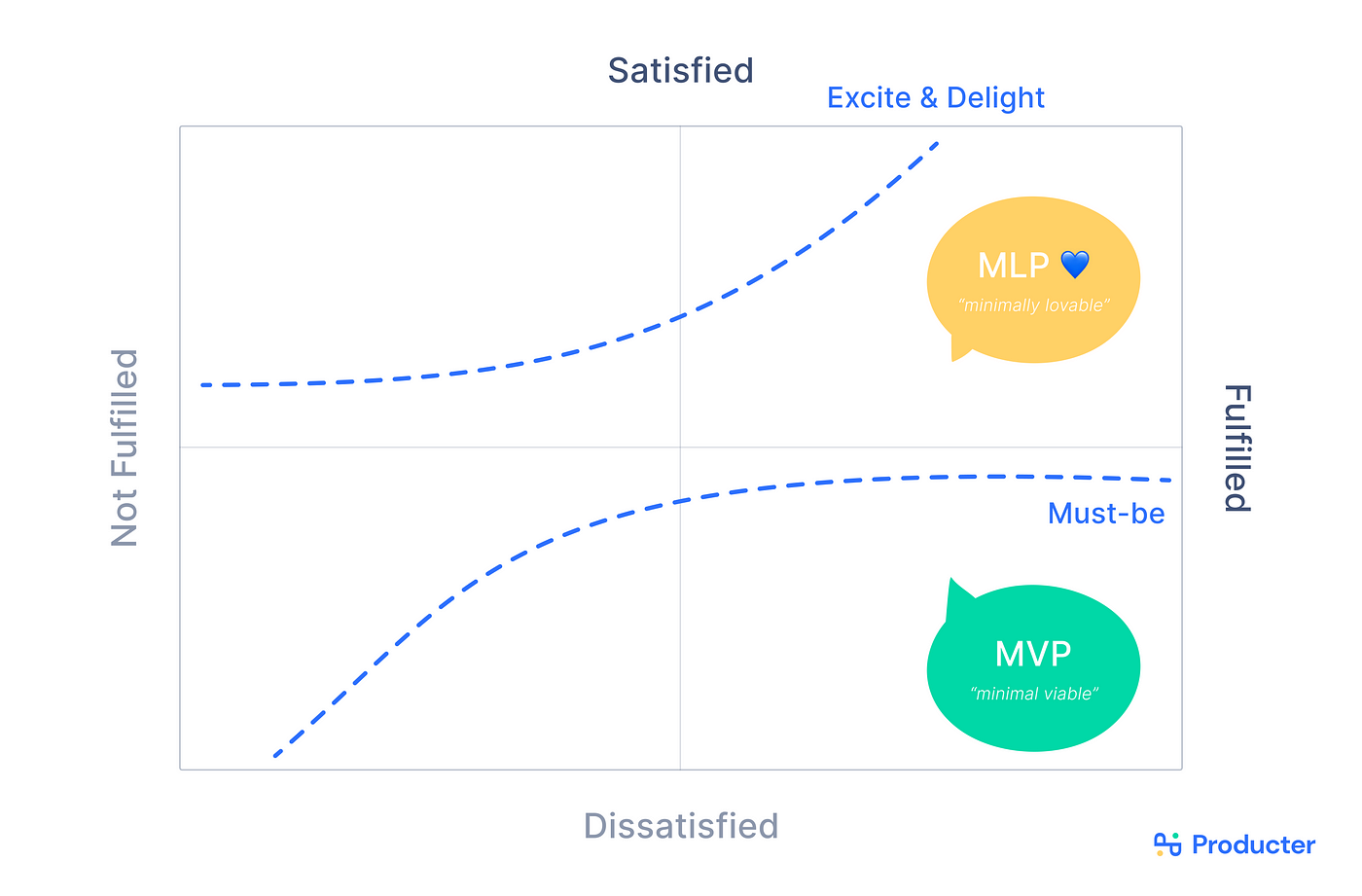
To sum up, MVP allows you to get a feel for your customer’s interest in your product without fully developing it. Rather than wasting time and money on a product that will not succeed in the market, it is better to find out sooner whether your product will appeal to customers.
Producter is a product management tool designed to become customer-driven.
It helps you collect feedback, manage tasks, sharing product updates, creating product docs, and tracking roadmap.






